
- #Adding a certificate for a vpn mac how to
- #Adding a certificate for a vpn mac install
- #Adding a certificate for a vpn mac password
- #Adding a certificate for a vpn mac free
At this point, any OS X service that uses SSL and the OS X keychain will trust any certificates issued by this CA. If you do a search now for the name of the certificate, it will have a blue + symbol and indicate it is a certificate that is marked as trusted for all users.
#Adding a certificate for a vpn mac password
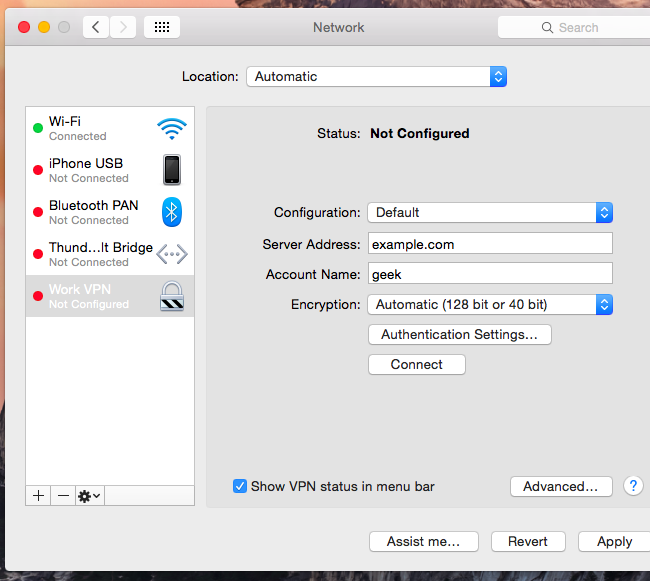
Provide the administrator password again and the System keychain will be updated. Finally, click the "Always Trust" button. Once you have examined the details, expand the Trust section and choose "Always Trust" for both "X.509 Basic Policy" and the "When using this certificate" pull-down. Expand the Details section to view the details of the root CA you will want to verify the details of the certificate, especially the Signature, to ensure it matches with the information you have been provided.

Here you must select the trust settings for this CA. The next window asks whether or not you want the computer to trust certificates from this CA in the future. You will be prompted for your administrator password. When asked which keychain to add the certificate to, select the System keychain from the pull-down window.
crt file and Keychain Access will open with the Add Certificate window. To begin, obtain the SSL certificate for the Certificate Authority (from an administrator or from the CA's Web site). This is especially true for work situations where a business has an internal Certificate Authority used for internal sites.
#Adding a certificate for a vpn mac install
Because of this, it may be desirable to install that particular Certificate Authority's root certificate on the system.
#Adding a certificate for a vpn mac free
This is what made certificate authorities so necessary - they did the legwork of verifying the owner of a site and also had root certificates present in all major browsers, meaning you could connect to a site without being prompted because your browser recognized the authority that signed the certificate, and could make sure it was valid.īecause using SSL is useful for more than just banking and e-commerce, and it is so expensive, other Certificate Authorities have begun offering cheap or free certificates but they may not have a root certificate present on the operating system or in the browser. It is easy enough to create a self-signed certificate, but when doing so, any visitor to your site has to trust that the certificate is valid and that they are actually connecting to your site. Unfortunately for those running online services that require encryption, or even those who want encryption for their site, a hefty price tag has always accompanied obtaining a certified SSL certificate. HTTPS, or HTTP over SSL, is something we use for logging into Web sites, online banking, e-commerce, and more. Secure communication over the Web is something we have taken for granted over the last number of years.
#Adding a certificate for a vpn mac how to
Vincent Danen shows you how to add a Certificate Authority's root certificate on an OS X system, allowing any OS X service that uses SSL and the OS X keychain to trust any certificates issued by the CA.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
